Understanding Gait Training for Balance Mastery
Balancing and walking are critical functions that can be significantly impacted by various neurological conditions. Effective gait training is essential for individuals aiming to regain or improve these abilities.
Importance of Gait Training in Neurological Physiotherapy
Gait training plays a pivotal role in neurological physiotherapy. It helps individuals improve their walking abilities by focusing on muscle strength, coordination, and balance. This is particularly beneficial for patients dealing with conditions like stroke rehabilitation, multiple sclerosis physiotherapy, and Parkinson’s disease rehabilitation. Through targeted exercises, we can help patients retrain their muscles and nervous systems, promoting better balance and reducing the risk of falls.
| Condition | Benefits of Gait Training |
|---|---|
| Stroke | Improved muscle strength and coordination |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Enhanced balance and reduced spasticity |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Better gait speed and stability |
Common Challenges in Gait and Balance
For many individuals undergoing neurological physiotherapy, there are several challenges in achieving optimal gait and balance. Common issues include muscle weakness, spasticity, and impaired coordination. Conditions like spinal cord injury rehabilitation and cerebral palsy physiotherapy often present unique challenges that require customized training programs.
Muscle weakness can result from a variety of conditions, necessitating targeted strengthening exercises. Spasticity, which can cause muscle stiffness and involuntary spasms, often requires specific techniques such as spasticity management. Additionally, impaired coordination and balance can be addressed through exercises designed to enhance neuromuscular control and proprioception, often included in vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
| Challenge | Affected Conditions | Suggested Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Weakness | Stroke, Spinal Cord Injury | Strengthening exercises |
| Spasticity | Cerebral Palsy, Multiple Sclerosis | Spasticity management techniques |
| Impaired Coordination | Ataxia, Parkinson’s Disease | Proprioceptive and neuromuscular exercises |
By understanding the importance of gait training and recognizing the common challenges faced, we can develop effective rehabilitation strategies. This ensures that individuals receive the best possible care tailored to their specific needs, helping them achieve balance mastery.
Essential Elements of Gait Training
Gait training is a critical component of neurological physiotherapy, aimed at enhancing balance and mobility. We will explore the essential elements that contribute to effective balance and gait training, including strengthening muscles for stability, improving coordination and balance, and enhancing flexibility and range of motion.
Strengthening Muscles for Stability
Strong muscles provide the foundation for stable and effective movement. In gait training, it’s vital to focus on strengthening the muscles that support posture and locomotion. Exercises targeting the core, legs, and lower back will enhance stability and improve overall gait.
Activities such as squats, lunges, and calf raises are essential. These exercises not only build muscle but also enhance neuromuscular coordination.
| Exercise | Muscle Group Targeted | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Squats | Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Glutes | 10-15 |
| Lunges | Quadriceps, Hamstrings, Glutes | 10-12 (each leg) |
| Calf Raises | Gastrocnemius, Soleus | 12-15 |
For individuals recovering from neurological conditions such as stroke rehabilitation or multiple sclerosis physiotherapy, strengthening exercises need to be tailored to their capabilities and progress.
Improving Coordination and Balance
Coordination and balance are crucial for safe and effective movement. Gait training incorporates exercises that challenge these aspects, helping individuals improve their walking patterns and prevent falls.
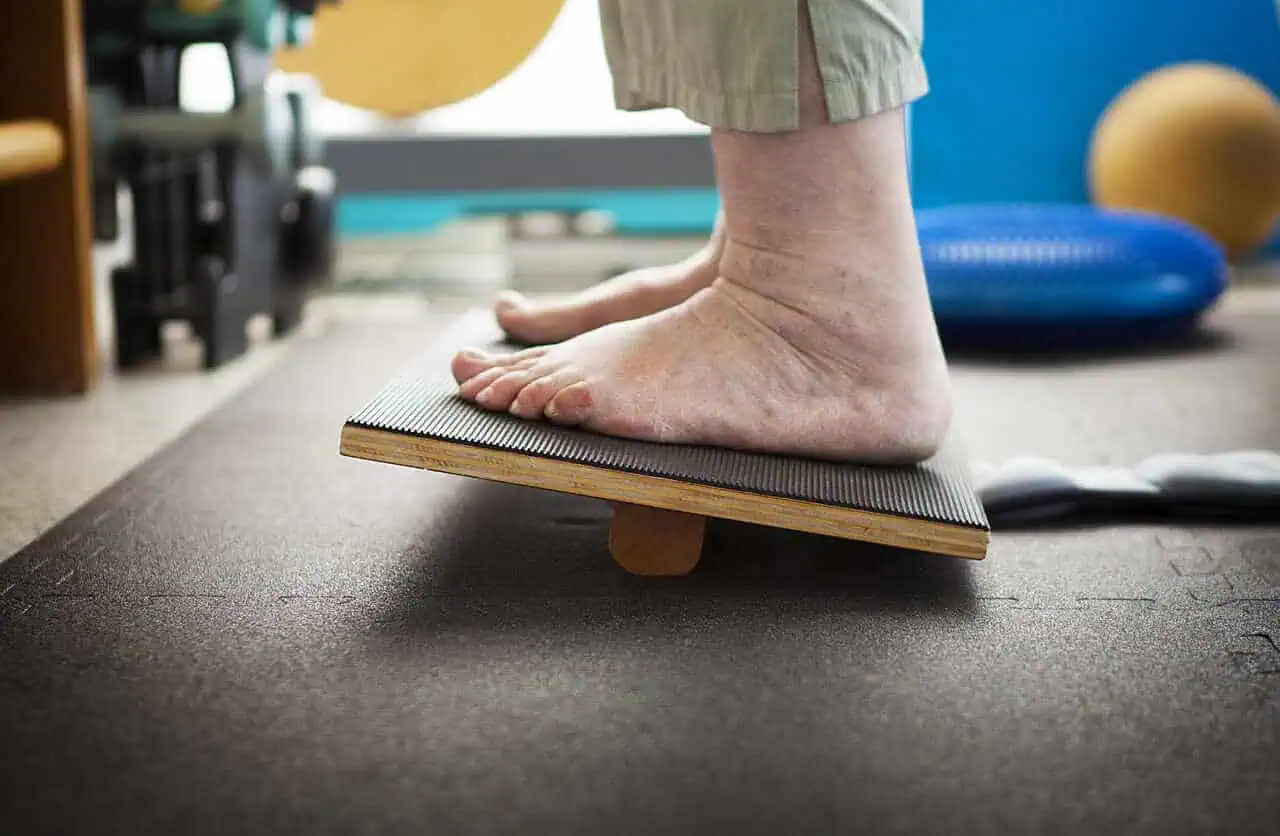
Activities such as standing on one leg, tandem walking, and balance board exercises are beneficial. These tasks help retrain the body’s muscle memory and improve proprioception.
| Exercise | Balance Focus | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| One-Leg Stand | Static Balance | 30 seconds (each leg) |
| Tandem Walking | Dynamic Balance | 2 minutes |
| Balance Board | Overall Balance | 3-5 minutes |
Neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease rehabilitation and vestibular rehabilitation therapy greatly benefit from these balance-focused activities.
Enhancing Flexibility and Range of Motion
Flexibility and range of motion are essential for functional mobility. Stretching exercises that target the major muscle groups and joints ensure that the body moves efficiently and without restriction.
Flexibility exercises can include hamstring stretches, calf stretches, and hip flexor stretches. These activities keep the muscles and joints supple, reducing the risk of injuries and enhancing overall gait performance.
| Exercise | Muscle Group Targeted | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Hamstring Stretch | Hamstrings | 30 seconds (each leg) |
| Calf Stretch | Gastrocnemius, Soleus | 30 seconds (each leg) |
| Hip Flexor Stretch | Hip Flexors | 30 seconds (each leg) |
Enhancing flexibility is particularly important for those undergoing spinal cord injury rehabilitation or cerebral palsy physiotherapy, as these activities can significantly impact mobility.
By incorporating these essential elements—strengthening muscles, improving coordination and balance, and enhancing flexibility—into gait training programs, we can achieve balance mastery for individuals across various neurological conditions. This holistic approach ensures coordinated, safe, and stable movement for improved quality of life.
For further details about specific conditions and tailored therapy options, explore our articles on motor neuron disease therapy and functional electrical stimulation (fes).
Techniques for Effective Gait Training
Developing effective techniques for balance and gait training is crucial for those undergoing neurological physiotherapy. Let’s explore some of the key methods that can aid in achieving balance mastery.
Weight Shifting Exercises
Weight shifting exercises play a fundamental role in gait training. These exercises enhance our ability to control balance by encouraging deliberate movements of body weight from one side to the other. This helps improve stability and coordination. For example, lateral weight shifts, where we move side to side, and anterior-posterior weight shifts, where we move forward and backward, are commonly used.
| Exercise Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Lateral Weight Shifts | Enhances side-to-side control |
| Anterior-Posterior Shifts | Improves forward-backward balance |
Performing these exercises regularly can significantly improve our balance and reduce the likelihood of falls.
Walking Aids and Assistive Devices
Walking aids and assistive devices are essential tools in balance and gait training, especially for individuals with conditions such as stroke rehabilitation or multiple sclerosis physiotherapy. These devices provide the necessary support to maintain proper posture and aid in mobility.
Common walking aids include:
- Canes
- Walkers
- Crutches
These tools can be adjusted to fit our specific needs, ensuring safe and effective gait training. It’s important to work closely with our physiotherapist to select the appropriate device and learn how to use it correctly.
Functional Tasks Practice
Functional tasks practice involves integrating everyday activities into our training routine. This type of training is essential for improving our ability to perform daily tasks with greater balance and stability. Activities such as standing from a seated position, climbing stairs, and walking on uneven surfaces are examples of functional tasks.
By incorporating these activities into our training, we can simulate real-world scenarios and improve our overall functional mobility. For more detailed exercises and strategies, visit our article on functional tasks practice.
These techniques, when applied consistently and correctly, can greatly enhance our balance and gait training efforts. To explore more about specific conditions and rehabilitation methods, you can visit our related articles on parkinsons disease rehabilitation, spinal cord injury rehabilitation, and neuromuscular rehabilitation.
Incorporating Balance Into Daily Life
Incorporating balance training into daily life plays a critical role in mastering gait and balance. It ensures continuous progress and risk reduction. Here are some essential strategies:
Home Exercises for Continued Progress
Continuing balance training at home helps to maintain and improve gains achieved during neurological physiotherapy sessions. These exercises are designed to strengthen muscles, enhance coordination, and improve overall stability.
| Exercise | Description | Repetitions | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heel-to-toe walk | Walk in a straight line, placing one foot directly in front of the other | 10 steps | 3 times/day |
| One-leg stand | Balance on one leg, holding onto a support if needed | 30 seconds/leg | 2 times/day |
| Seated leg lifts | Lift one leg while seated, alternate legs | 10 lifts/leg | 2 times/day |
Integrate these exercises and adjust as improvements are noted. For more specific guidance, visit our article on vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
Strategies for Fall Prevention
Preventing falls is paramount for those undergoing gait training. By adopting effective strategies, the risk of falls can be significantly minimized.
- Home Modifications: Remove tripping hazards such as loose rugs and clutter.
- Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that provide good support and have non-slip soles.
- Assistive Devices: Use walking aids like canes or walkers as advised by a physiotherapist.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in exercises that enhance strength and balance, such as those listed above.
For more in-depth strategies specific to conditions like parkinson’s disease rehabilitation or stroke rehabilitation, explore our related resources.
Creating a Safe Environment for Mobility
A safe environment is crucial for fostering confidence and reducing the risk of accidents. Here are some measures to ensure safety:
- Adequate Lighting: Ensure all areas are well-lit to avoid tripping.
- Grab Bars and Handrails: Install in bathrooms and along staircases.
- Clear Pathways: Keep walkways free from obstacles and hazards.
- Non-Slip Mats: Place in areas prone to wetness, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
By creating a safe living space, individuals can confidently practice their balance and gait exercises, contributing to long-term stability and mobility. For additional strategies tailored to specific neurological conditions, refer to our articles on functional movement disorders physiotherapy and muscle weakness rehabilitation.
Integrating these practices and consistently following them can greatly enhance balance mastery, contributing to an overall improved quality of life.
Progress Monitoring and Adjustments
Accurately tracking progress and making necessary adjustments are critical aspects of successful balance and gait training. Below, we delve into the methods for monitoring improvements and adjusting training programs to ensure long-term mastery.
Tracking Gait and Balance Improvement
For effective gait and balance training, it’s essential to monitor progress consistently. We can track improvement through various methods, including assessments, gait analysis, and recording performance metrics.
Assessment Tools:
- Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test
- 10-Meter Walk Test
- Functional Gait Assessment (FGA)
| Assessment Tool | Measurement Focus | Baseline | Current Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| TUG Test | Mobility | 15 secs | 12 secs |
| 10-Meter Walk | Walking Speed | 1.4 m/s | 1.7 m/s |
| FGA | Gait Function | 18/30 | 24/30 |
These evaluations can help identify areas that need further improvement. For more detailed assessment techniques, see our articles on stroke rehabilitation and multiple sclerosis physiotherapy.
Adjusting Training Programs as Needed
Individualized adjustment of training programs is necessary to address specific needs. As patients progress, evaluations may indicate the need for modifications such as increasing the complexity of exercises.
- Increase Complexity: Incorporate multi-tasking exercises, such as balancing on one foot while catching a ball.
- Adjust Intensity: Modify resistance levels and increase repetitions for strengthening exercises.
- Incorporate Technology: Utilize biofeedback mechanisms and functional electrical stimulation (FES) to enhance training.
Reviewing progress every few weeks can help to tailor the program better to the individual’s needs. For specific neurological conditions, refer to our articles on Parkinson’s disease rehabilitation and spinal cord injury rehabilitation.
Working Towards Long-Term Balance Mastery
Achieving long-term balance and gait mastery involves sustained efforts and regular reassessments. It is important to integrate various strategies that adapt over time as individuals make progress.
- Continual Learning: Patients should be educated on the importance of maintaining their exercise routines.
- Regular Re-evaluation: Schedule regular re-evaluations to ensure consistent progress and to make any necessary changes.
- Supportive Environment: Create an environment conducive to exercising regularly and safely at home.
Long-term mastery requires a collaborative approach between patients and therapists. For comprehensive strategies, refer to articles on neuromuscular rehabilitation and vestibular rehabilitation therapy.
Utilizing these strategies ensures that gait and balance training is effective and sustainable, setting the groundwork for long-term success in neurological physiotherapy.