Get a Customized Plan to Overcome Scoliosis!
Scoliosis Cambridge
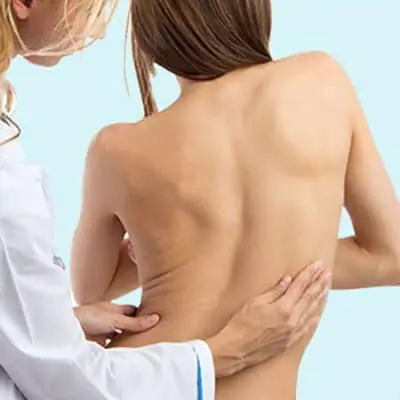
Cambridge Physiotherapy is the closest place to go to when you or your child is living with Scoliosis. This clinic now offers Scoliosis Rehab using the latest techniques in the Schroth method.
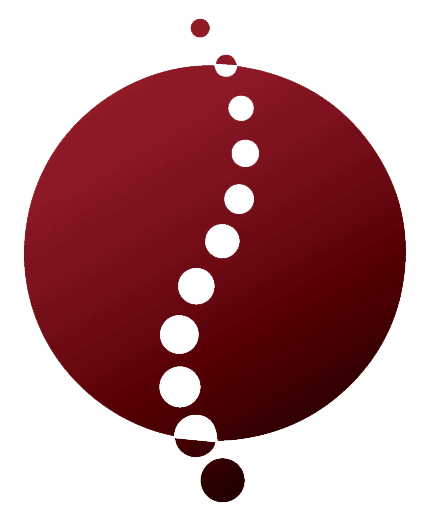
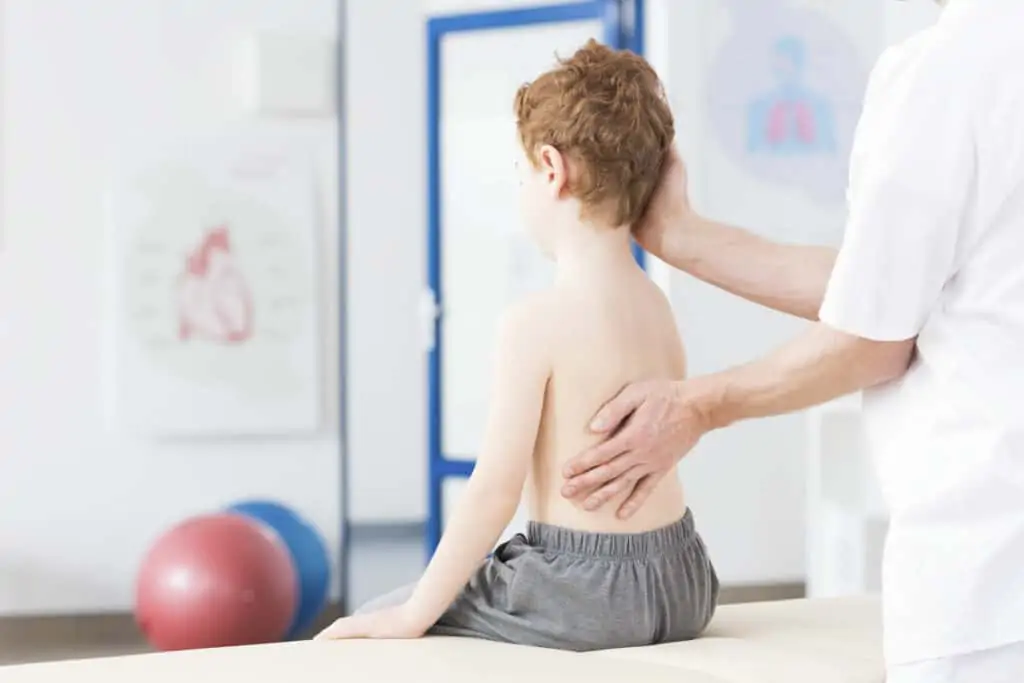
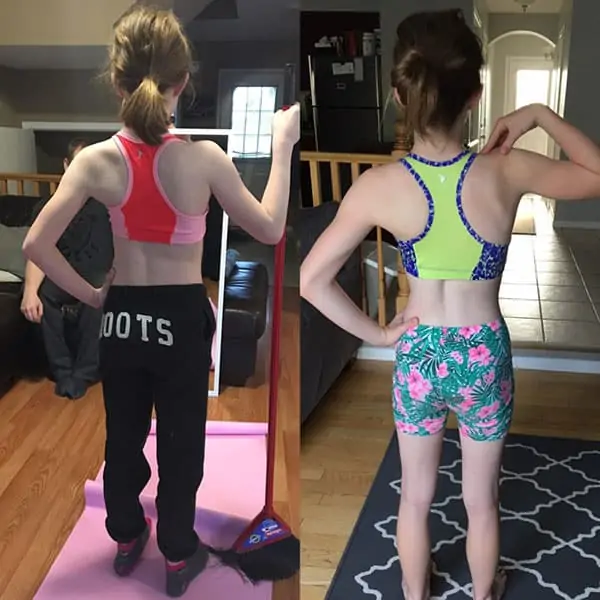
Scoliosis is an alteration of the curve of the spine away from the normal, with a lateral (side to side) curvature and rotation of the vertebra. For a diagnosis of Scoliosis, the curve must be greater than 10 degrees. At least 2-4% of children under the age of 16 will be diagnosed with idiopathic scoliosis, meaning there is no known reason for scoliosis.
The traditional method was the ‘wait & see’ approach which may or may not include bracing depending on the degree of the curvature. This would then be followed by surgery if the curve progresses to 45 degrees and above. We now know that the ‘wait & see’ approach is not the best way to go. Early intervention is key.
Here at Cambridge Physio, we use the Schroth method of Scoliosis physiotherapy to help those living with scoliosis lead an optimal life.
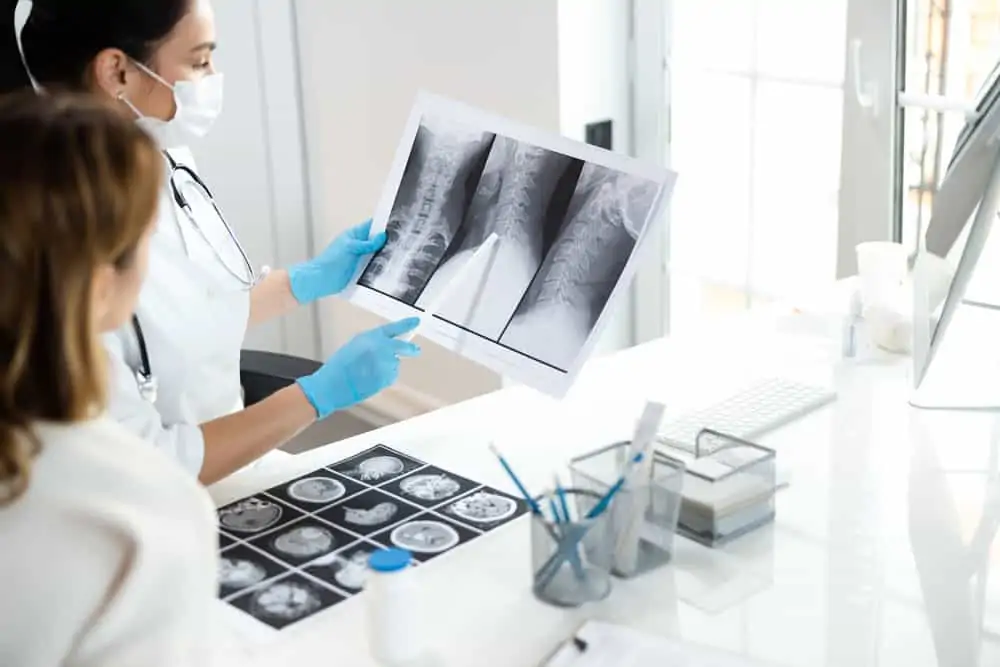
The Schroth Method of treating Scoliosis is a Physiotherapeutic treatment that incorporates three-dimensional exercises that are specific to different curves depending on the diagnosis, Xrays and Cobb angle.
The goals of these exercises are:
- Correct posture and improve postural awareness
- Stabilize the Spine & Stop the Progression
- Educate correct positions while doing activities of daily living
- Improve breathing capacity
- Improve body mechanics
- Increase strength
- Assist with pain reduction
For patients wearing a brace, studies have shown that bracing along with Schroth Physiotherapy is more effective than bracing alone (article in the resource section).
Idiopathic Scoliosis can be defined as a complex three-dimensional deformity of the spine and trunk, which appears in apparently healthy children, and can progress in relation to multiple factors during any rapid period of growth. Specific prevention of idiopathic scoliosis is not possible, because its ultimate cause is unknown; however, there is a high consensus about the necessity to prevent curve progression. For most scoliosis specialists, conservative management of idiopathic scoliosis is related to bracing, and its main objective is to prevent curve progression to a more or less arbitrary critical point, where surgical correction would be indicated. Scoliosis-specific rehabilitation is more comprehensive than this and has gained an increased interest during the past several years.
Excerpt from Rigo and Grivas. “Rehabilitation schools for scoliosis” thematic series: describing the methods and results. scoliosis 2010 5:27.
Generally speaking, the objectives of scoliosis rehabilitation are to maintain function and prevent symptoms in the short and long term. More specifically, scoliosis rehabilitation’s goal is to prevent curve progression, while trying to correct the spinal and trunk deformity in the long term, and to prevent the health-related quality of life from deteriorating, while trying to improve it. Scoliosis Rehabilitation follows a model including:
- Correct diagnosis and evaluation of the patient to make a treatment decision oriented to the scoliosis patient.
- Treatment is based on: observation (with rational use of X-rays), education, specific physical exercises, and bracing.
- Quality control and evaluation of the results.
Parents, if you notice your child’s head is tilted to one side, or there is a prominence on their back, their shoulders are not level, a shoulder blade is higher than the opposite one, leans to one side, or their waist is uneven, a visit to the Family Physician or a Specialist will help with further examination and / or diagnosis.
Learn about how we support scoliosis patients in the Waterloo and Guelph areas.
For more information about scoliosis
http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0168746
https://scoliosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13013-016-0076-9
https://scoliosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/
University of Alberta Press release:
https://www.ualberta.ca/rehabilitation/news/2017/january/specialized-physical-therapy-helps-teens-with-scoliosis-get-ahead-of-the-curve
The Schroth Method:
http://www.schrothmethod.com/christa-lehnert-schroth
Bracing and Therapy:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4132192/
Support groups in Ontario:
https://www.curvygirlsscoliosis.com/canada—ontario
FAQ Section
Yes, people with scoliosis can live normally. With the right treatment and management, people with scoliosis can lead a healthy and active lifestyle. The key is to find the right treatment plan that works for you. This may include physical therapy, bracing, or even surgery depending on the severity of your condition. It is important to stay active and maintain a healthy diet in order to keep your spine healthy and strong.
It is not possible to fully cure adult scoliosis but with the right treatment, the symptoms can be minimized. Depending on the severity of the condition, a combination of treatments such as physical therapy, bracing, and surgery may be necessary to correct scoliosis. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve posture. Bracing can help reduce the curvature of the spine and prevent further progression of scoliosis. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to fully correct the curvature of the spine.
Cambridge
Physiotherapy & Rehab Center
895 Langs Dr Unit #2, Cambridge, ON N3H 5T6, Canada
Hours:
Monday: 9AM-5PM
Tuesday 9AM-8PM
Wednesday: 9AM-5PM
Thursday: 9AM-8PM
Friday: 9AM-5PM
Saturday & Sunday: Closed