Understanding Muscle Weakness Rehabilitation
Importance of Muscle Rehabilitation
Muscle rehabilitation is essential for individuals experiencing muscle weakness due to various neurological conditions. Effective rehabilitation helps restore muscle function, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life. Our approach focuses on tailored strategies that address individual needs, ensuring optimal recovery.
Key benefits of muscle rehabilitation:
- Improved strength and endurance
- Enhanced coordination and balance
- Reduction in muscle atrophy
- Increased independence in daily activities
By incorporating advanced techniques and personalized care, we aim to achieve the best possible outcomes for those undergoing muscle weakness rehabilitation.
Factors Contributing to Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness can result from a multitude of factors, often linked to neurological disorders. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing an effective rehabilitation plan.
Primary contributors to muscle weakness:
- Neurological Conditions: Diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can disrupt nerve signals, leading to muscle weakness.
- Injuries: Trauma to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves can significantly impair muscle function. Spinal cord injury rehabilitation is vital for those affected.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like Guillain-Barré syndrome and myopathies contribute to muscle deterioration.
- Genetic Disorders: Congenital conditions such as cerebral palsy affect muscle control and strength.
- Metabolic Imbalances: Deficiencies in essential nutrients can weaken muscles, necessitating proper dietary support.
| Condition | Common Effect on Muscles |
|---|---|
| Multiple Sclerosis | Muscle Fatigue and Spasticity |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Rigidity and Reduced Strength |
| Stroke | Hemiparesis (Weakness on One Side) |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Paralysis Below Injury Site |
| Guillain-Barré Syndrome | Ascending Muscle Weakness |
Effective muscle weakness rehabilitation begins with accurately diagnosing these underlying causes. For more detailed information, visit our articles on diagnostic tests and procedures, and the importance of individualized exercise programs. Understanding these elements is crucial for successfully revitalizing muscle strength and function.
Assessment and Diagnosis
A thorough assessment and accurate diagnosis are crucial steps in the journey of muscle weakness rehabilitation. These steps help healthcare professionals to create an effective and personalized rehabilitation plan.
Initial Evaluation by Healthcare Professionals
Our initial evaluation begins with a comprehensive consultation with healthcare professionals. This involves a detailed review of the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and any previous treatments. The physical examination checks muscle strength, range of motion, and reflexes.
During the evaluation, healthcare professionals also take note of any neurological symptoms that might be present. This helps in determining whether the muscle weakness is due to issues such as stroke rehabilitation, multiple sclerosis physiotherapy, or other conditions needing specialized treatment.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures for Muscle Weakness
To further pinpoint the cause of muscle weakness, various diagnostic tests and procedures are employed. These aid in understanding the underlying issues and tailoring the rehabilitation process accordingly.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Electromyography (EMG) | Assess electrical activity in muscles | Inserts a fine needle electrode into the muscle to measure electrical activity |
| Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) | Evaluate nerve function | Uses electrodes to stimulate nerves and measure the speed and strength of signals |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Visualize soft tissues, muscles, and nerves | Produces detailed images using magnetic fields and radio waves |
| Blood Tests | Identify underlying conditions | Checks for markers of inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, and autoimmune conditions |
| Muscle Biopsy | Examine muscle tissue | Involves taking a small sample of muscle tissue for laboratory analysis |
Combining these evaluations and diagnostic results facilitates the identification of specific conditions requiring targeted interventions, such as parkinsons disease rehabilitation, spinal cord injury rehabilitation, or spasticity management.
Understanding the significance of a precise diagnosis ensures that subsequent rehabilitation methods, whether through neuromuscular rehabilitation or neuroplasticity training, are both effective and safe for the patient. Consistent monitoring and adjustments to the plan are essential as the patient progresses in their journey to muscle recovery.
Developing a Rehabilitation Plan
Creating a rehabilitation plan tailored to individual needs is essential in muscle weakness rehabilitation. We will cover two crucial aspects: individualized exercise programs and physical therapy techniques to enhance muscle strength.
Individualized Exercise Program
An individualized exercise program is central to effective muscle weakness rehabilitation. It ensures that each patient’s unique needs are addressed, promoting optimal recovery. This program typically includes various exercises tailored to strengthen specific muscle groups and improve overall functional ability.
One approach is to categorize exercises based on the muscle groups they target. Here’s an example table showcasing different types of exercises:
| Muscle Group | Exercise Type | Frequency (per week) |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Body | Resistance Bands | 3 – 4 |
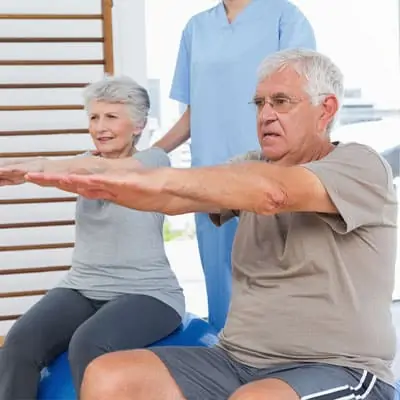
| Core | Stability Ball Exercises | 3 |
| Lower Body | Squats and Leg Press | 3 – 4 |
| Cardiovascular | Treadmill Walking | 5 – 6 |
Internal links within the exercise program can guide you to specific techniques and additional information:
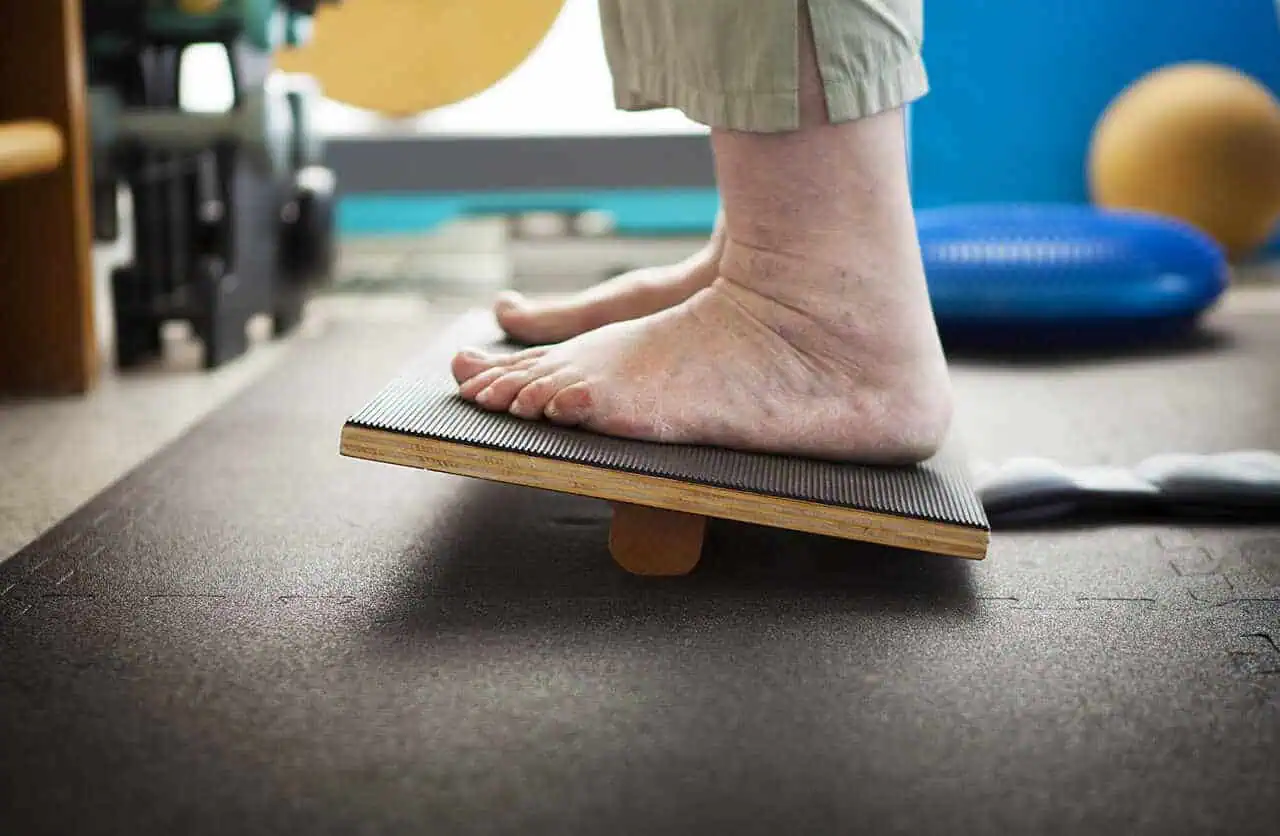
- For exercises targeting functional movement, explore balance and gait training.
- To understand the role of electrical stimulation, check functional electrical stimulation (fes).
Physical Therapy Techniques for Muscle Strength
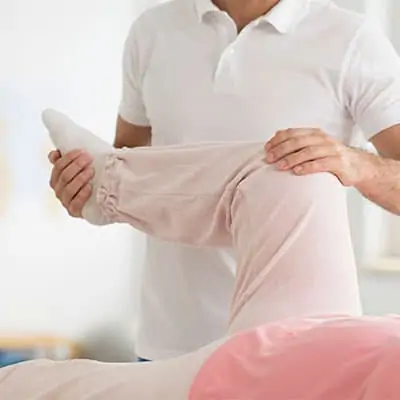
Physical therapists employ various techniques designed to restore muscle strength and improve mobility. These techniques are customized to meet the needs of patients based on their condition, severity of muscle weakness, and overall health.
Key physical therapy techniques include:
- Therapeutic Exercise: Exercises aimed at improving strength, range of motion, and endurance. Techniques such as progressive resistance exercises (PRE) are often used.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques like massage and joint mobilization to alleviate pain and improve muscle function.
- Neuromuscular Reeducation: Techniques to retrain and strengthen the connections between the muscles and the nervous system. This includes proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF).
- Functional Training: Exercises that mimic daily activities to enhance functional performance. This can include sit-to-stand exercises and balance work.
To further understand neurological physiotherapy techniques, visit articles like neuromuscular rehabilitation and neuroplasticity training.
By combining individualized exercise programs with specialized physical therapy techniques, we can address the multifaceted needs of those facing muscle weakness. Tailoring these strategies enhances their efficacy, making a significant impact on the patient’s journey towards recovery.
Dietary and Nutritional Support
To effectively address muscle weakness rehabilitation, we must consider the role of nutrition in the recovery process. Proper nutritional support is vital for rebuilding muscle strength and promoting overall recovery.
Importance of Nutrition in Muscle Recovery
Nutrition plays a crucial role in muscle recovery by providing the building blocks necessary for repair and growth. Adequate intake of essential nutrients supports muscle protein synthesis, reduces inflammation, and enhances overall healing. A well-balanced diet ensures the body receives the vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients required for optimal function.
Muscle recovery benefits from the following key nutrients:
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy for physical activity and recovery.
- Fats: Support cell structure and hormone production.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Aid in various metabolic processes and tissue repair.
Nutritional Guidelines for Muscle Rehabilitation
To develop an effective nutritional plan for muscle rehabilitation, consider the following guidelines. These guidelines ensure the body receives adequate nutrition to support muscle recovery.
| Nutrient | Recommended Intake | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 1.2 – 2.0 g/kg of body weight per day | Promotes muscle repair and growth |
| Carbohydrates | 45-65% of total daily calories | Provides energy for physical activities |
| Fats | 20-35% of total daily calories | Supports cell structure and hormone production |
| Vitamin D | 600-800 IU per day | Supports bone health and muscle function |
| Calcium | 1,000-1,200 mg per day | Essential for muscle contraction and bone strength |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | 250-500 mg per day | Reduces inflammation and supports muscle recovery |
Incorporating the above nutrients into a balanced diet promotes effective muscle recovery. For individuals undergoing stroke rehabilitation, multiple sclerosis physiotherapy, or spinal cord injury rehabilitation, tailored nutrition plans are imperative for optimal healing.
It’s critical to work with healthcare professionals to create an individualized nutritional plan that meets specific needs. This comprehensive approach ensures that our patients receive the best possible support for their muscle weakness rehabilitation journey. For additional resources, consider exploring myopathy rehabilitation and neuroplasticity training for further insights into rehabilitation strategies.
Technology and Innovation in Muscle Rehabilitation
In the field of muscle weakness rehabilitation, technology and innovation play a pivotal role. Utilizing advanced tools and techniques can significantly enhance the recovery process and improve outcomes for patients.
Assistive Devices and Equipment
Assistive devices and equipment are essential components in muscle rehabilitation. These tools are designed to aid patients in performing exercises that they might find challenging due to muscle weakness. Some of the most commonly used devices include:
- Exoskeletons: Wearable robotic suits that support and enhance movement.
- Electrical Stimulation Devices: Machines that use electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions.
- Resistance Bands and Weights: Equipment used to build muscle strength gradually.
Benefits of Various Assistive Devices:
| Device Type | Main Benefit |
|---|---|
| Exoskeletons | Enhances mobility and supports joint movement |
| Electrical Stimulation Devices | Stimulates muscle contractions and improves muscle function |
| Resistance Bands | Enhances muscle strength through controlled resistance |
| Weights | Gradually builds up muscle power and endurance |
For an in-depth look at how electrical stimulation can assist in muscle recovery, visit our guide on functional electrical stimulation (fes).
Advances in Neurological Physiotherapy
Advances in neurological physiotherapy have significantly impacted the way muscle weakness is treated. These innovations address the neurological aspects of muscle dysfunction, promoting better recovery and functional improvement. Some of these advances include:
- Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy: Uses VR environments to enhance motor learning and rehabilitation exercises.
- Robotic-Assisted Therapy: Employs robotic devices to perform repetitive movements crucial for muscle recovery.
- Neuroplasticity Training: Techniques designed to rewire the brain and improve motor function.
Advances in Neurological Physiotherapy:
| Technique | Core Advantage |
|---|---|
| Virtual Reality Therapy | Enhances engagement and provides diverse exercise scenarios |
| Robotic-Assisted Therapy | Delivers precise, repetitive movements for muscle strengthening |
| Neuroplasticity Training | Promotes brain adaptation and recovery of motor functions |
These methods are particularly useful in conditions such as stroke rehabilitation, multiple sclerosis physiotherapy, and spinal cord injury rehabilitation.
By utilizing these cutting-edge technological tools and innovative techniques, we can offer comprehensive and effective muscle weakness rehabilitation programs to aid patients in regaining their strength and improving their quality of life. To explore more strategies and methods in neurological physiotherapy, visit our detailed articles on neuroplasticity training and balance and gait training.
Maintaining Muscle Health
Long-term Rehabilitation Strategies
Maintaining muscle health is a continuous process that requires dedication and strategic planning. Long-term rehabilitation strategies are essential for those of us recovering from muscle weakness to regain and maintain our muscle strength and functionality. These strategies often include a combination of regular exercise, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Regular Exercise Regimen
A well-structured exercise program tailored to individual needs can significantly contribute to maintaining muscle health. This program should focus on a balance of strength training, aerobic exercises, and flexibility workouts. It’s crucial to gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercises to avoid overexertion.
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Strength Training | 3-4 times a week | 30-45 minutes |
| Aerobic Exercise | 3-5 times a week | 20-30 minutes |
| Flexibility Workouts | Daily | 10-15 minutes |
Preventive Measures to Avoid Muscle Weakness
Preventing muscle weakness requires a proactive approach. We must incorporate various preventive measures to safeguard our muscles against potential weakening.
Balanced Diet and Hydration
Nutrition plays a crucial role. A diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals supports muscle repair and growth. Staying hydrated is equally important as it helps maintain muscle function and prevent cramps.
| Nutrient | Source | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Lean meats, beans, nuts | Muscle repair and growth |
| Vitamin D | Sun exposure, fortified foods | Bone health and muscle function |
| Magnesium | Nuts, seeds, leafy greens | Muscle relaxation and contraction |
Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups help detect any early signs of muscle weakness. Healthcare professionals can perform assessments and recommend appropriate interventions. Diagnostic tests and procedures can be revisited for continuous optimization of the rehabilitation plan.
Ergonomics and Posture
Adopting proper ergonomics in daily activities can prevent muscle strain. Maintaining good posture during sitting, standing, and lifting heavy objects reduces the risk of muscle injuries.
Physical Therapy and Support
Ongoing physical therapy helps in monitoring progress and adjusting exercise plans as needed. Techniques such as functional electrical stimulation (FES) and balance and gait training are beneficial. Engaging in support groups or therapy sessions can offer additional motivation and guidance.
We need to stay informed about advancements in neurological physiotherapy, such as neuromuscular rehabilitation, to integrate new and effective methods into our routines. Maintaining muscle health is a lifelong commitment, essential for leading an active and fulfilling life.